Media Service
The Media Service enables you to manage large content catalogs as part of an OTT (over-the-top) streaming solution. It allows you to manage hundreds of thousands of media entities (Movies, TV shows, Seasons, Episodes, etc.), including license management for multiple regions.
It offers automated workflows to ingest media metadata and orchestrate the transcoding, encryption, packaging, and publishing of the related video assets and the import of image assets. The system is designed to handle valuable studio content in a secure way. It enables customers to validate and publish the metadata to the catalog service from where the content is available to all end-user devices.
The microservice backend and the microfrontend are available with their full source code as a part of the Mosaic Media Template. It enables you to use all the existing functionality and to fully adjust it to your business needs.
OTT Media Service container diagram
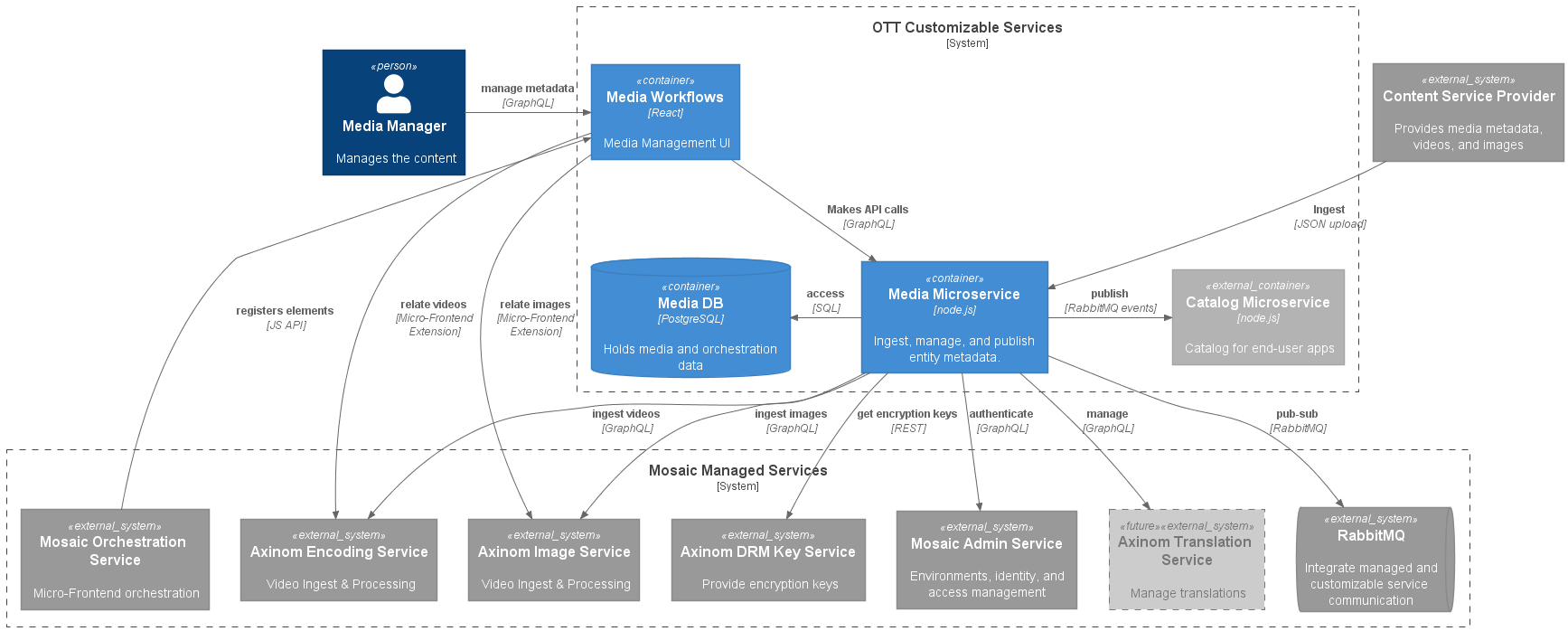
Frontend
The microfrontend workflows offer an intuitive GUI which is implemented in React. This GUI uses a common set of UI components, provided by the Mosaic UI library. Mosaic uses Piral as the microfrontends engine. The workflows are fully customizable as they use the reusable components of Mosaic. You could also add your own implementations. The microfrontend interacts with the media microservice backend via its GraphQL API.
Workflows
The media workflow project produces a package that gets loaded into the Orchestration Application to provide the OTT media stations, tiles on the homepage, and, potentially, some extensions. See the Mosaic developer documentation for a full description of how the microfrontends are registered.
The OTT media workflow package implements workflows to manage movies, TV shows, seasons, episodes, and collections. Each of them registers a tile on the homepage that starts the workflow to view and manage the corresponding entities. In addition to those tiles, the template also adds tiles for the ingest, snapshot registry, and settings for the movie and TV show genres.
Mosaic Media Template Homepage
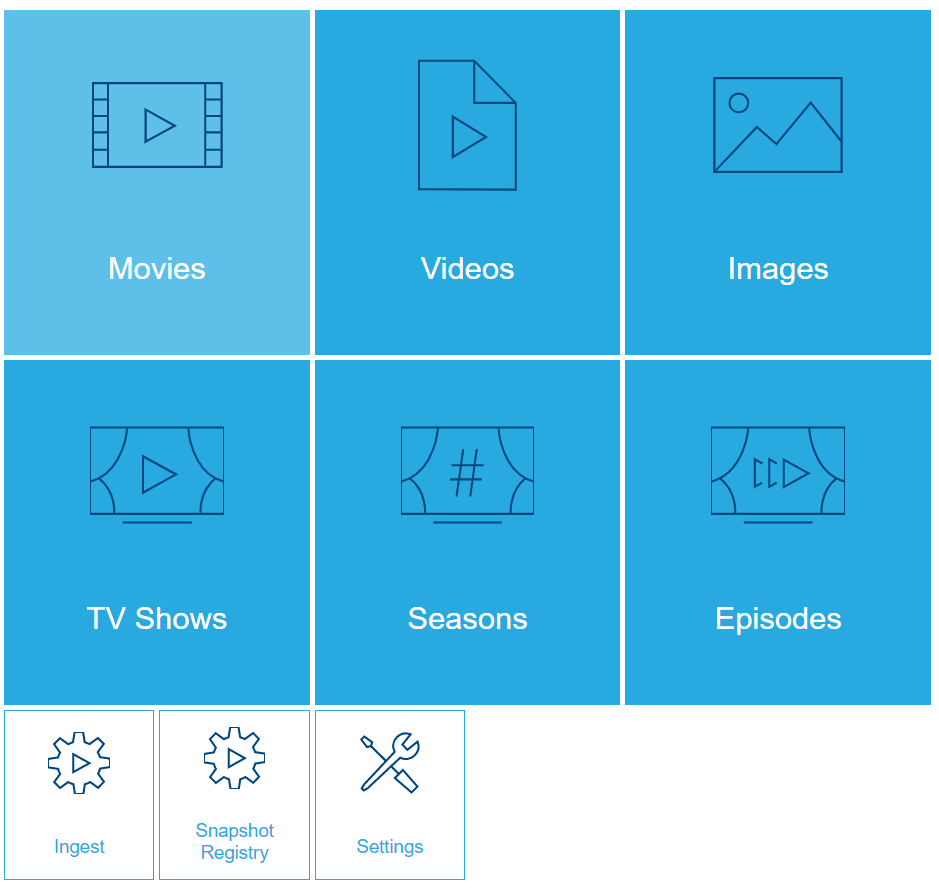
Movies
The definitions of all movie related stations reside inside the
Stations/Movies folder. Most of them consist of a React component file,
a GraphQL query definition file, and, potentially, a Sass styles file.
When a user selects the Movies tile on the homepage, the MoviesExplorer
will be loaded. The explorer station shows all the movies in the media
service in a sortable and filterable list. The filters, grid columns, and renderers
can be customized for your specific business needs or preferences.
Clicking one of the movies opens the details station of the movie. Additionally, there are also bulk operations available. For the movies, those include: to bulk create snapshots, publish or unpublish them, and delete multiple movies.
Mosaic Media Template Movie Details Workflow
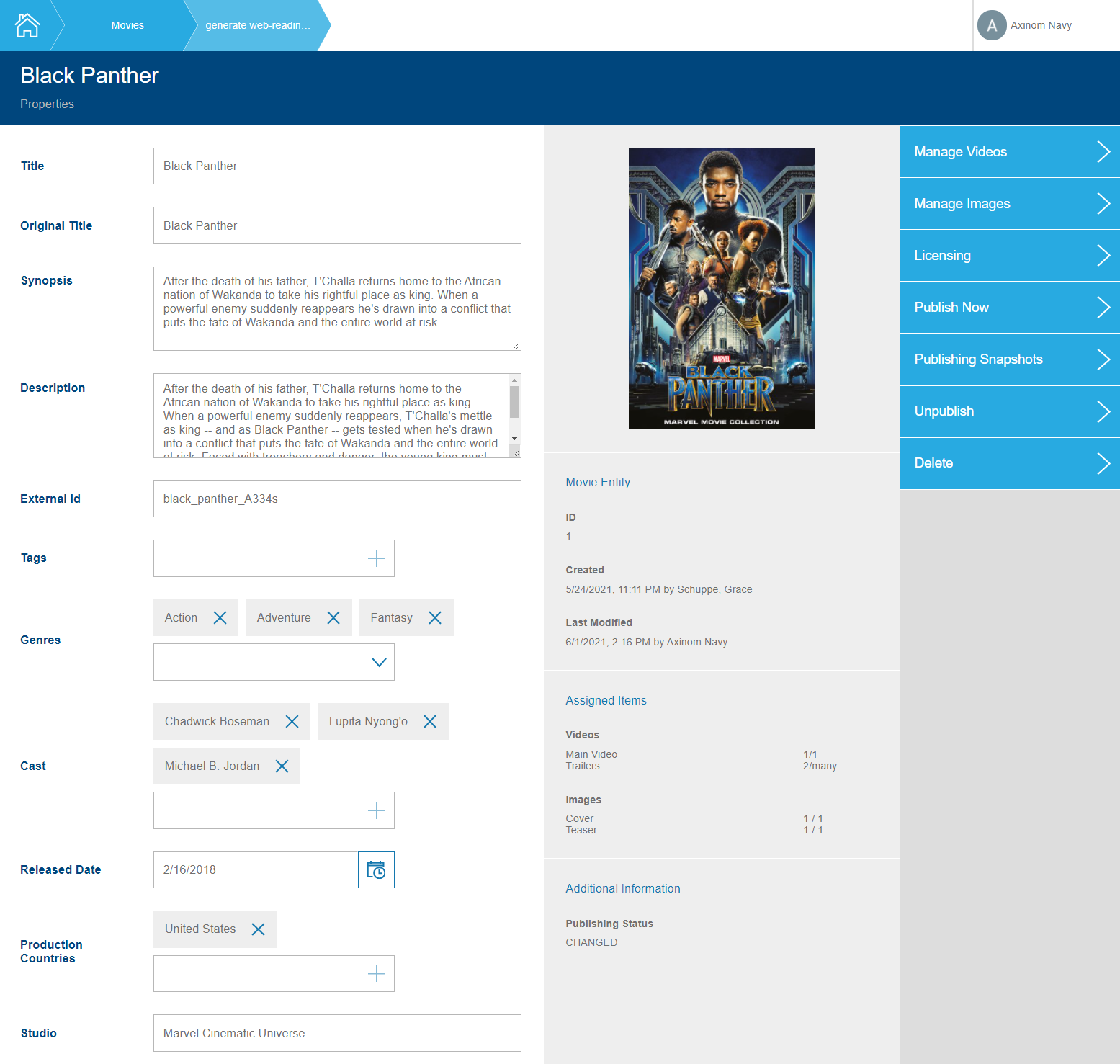
The MovieDetails station provides ways to change the details of a movie itself
(title, synopsis, description, etc.) but also to change its related data (tags, genres,
cast, etc.). The template uses controls from the Mosaic UI library but you can
easily create/use your own controls as well. In the MovieLicensing sub-station,
the licensing information can be managed and further customized.
The MovieVideoManagement and MovieImageManagement stations provide options
to manage the video and image assignments. The stations make use of extensions
provided by the (managed) Video and Image service that provide components for browsing
and selecting as well as displaying the metadata of the assigned videos and images,
so the stations just need to care for storing and updating the assigned element ids.
Images have a specific image type. The image management station uses this to allow
only images of a specific type to be assigned to the corresponding properties
(movie cover vs movie teaser).
The publishing process and snapshot overview and details section allow to publish and unpublish the movies. The snapshot overview and detail stations show the history of snapshots and publications and are fully customizable.
TV Shows
TV shows are collections of seasons that contain episodes. They are managed in a similar way to movies. Therefore, most of what was written in that section, applies here as well.
Mosaic Media Template TV Show Details Workflow
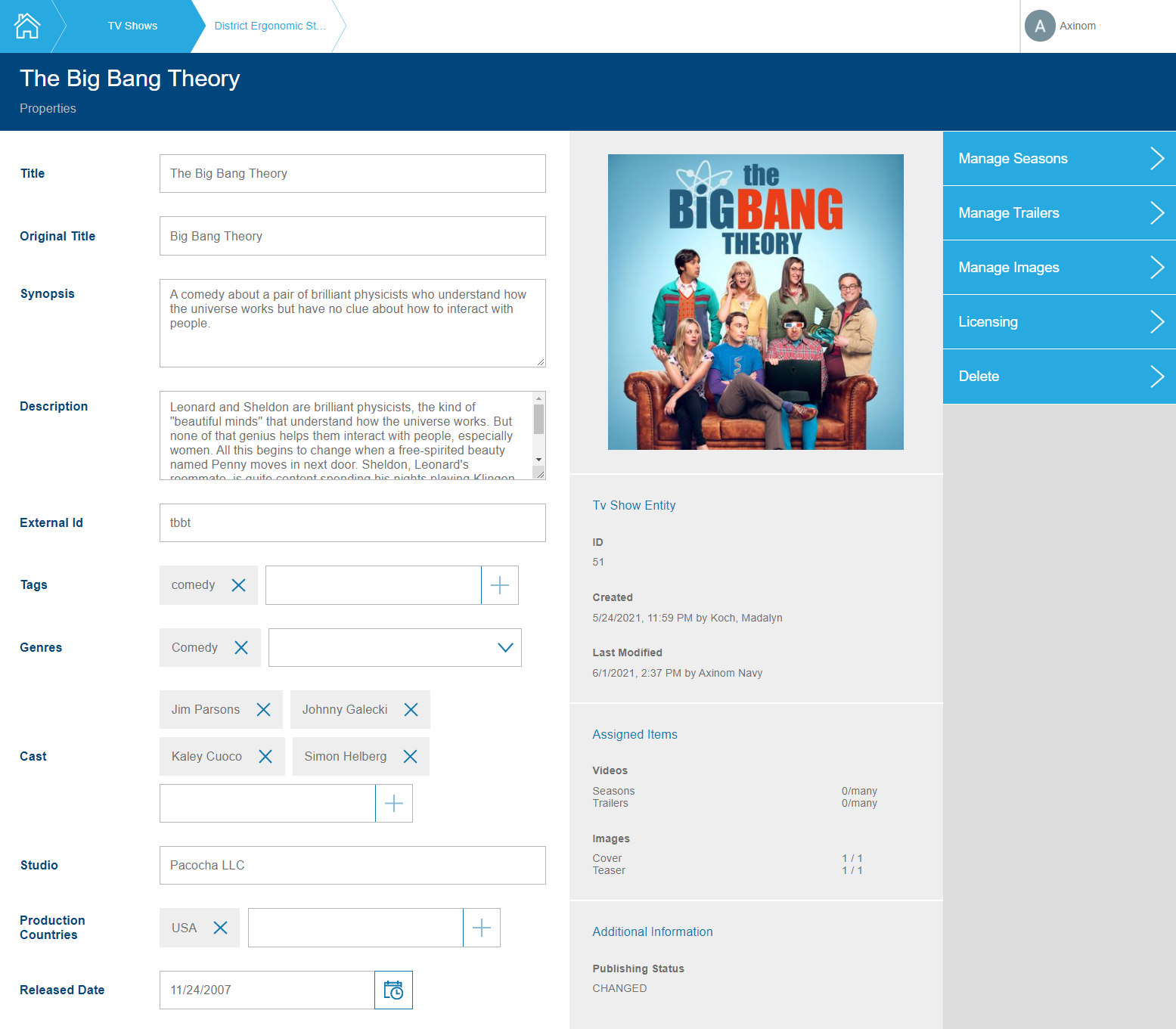
In addition to the stations that are also there for movies, the TV show includes the season management. Season, in turn, includes episodes. Both stations and the selection can be customized.
The station definitions are located in the Stations/TvShows, Stations/Seasons,
and Stations/Episodes folders.
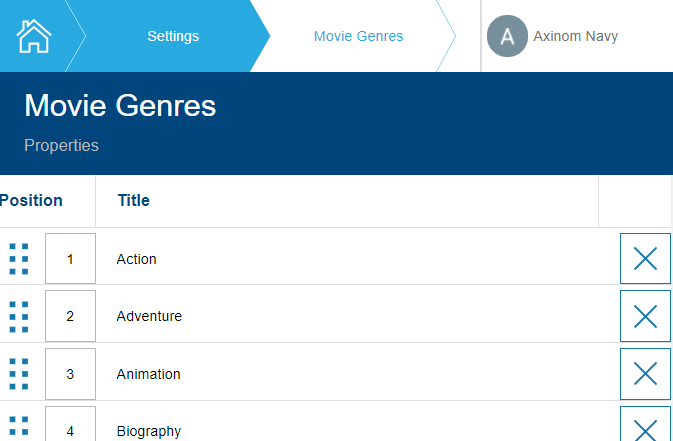
Genres
Movies and TV shows/seasons/episodes can select the genres to which they
belong. The available genres and their sort order are managed in the
Settings. There is one list of genres for movies and another list of
genres for TV shows, seasons, and episodes from which they can select.
Customizations can be done in the Stations/Movies/MovieGenres and
Stations/TvShows/TvShowGenres folders, respectively.
Mosaic Media Template Movie Genres Workflow
Ingest
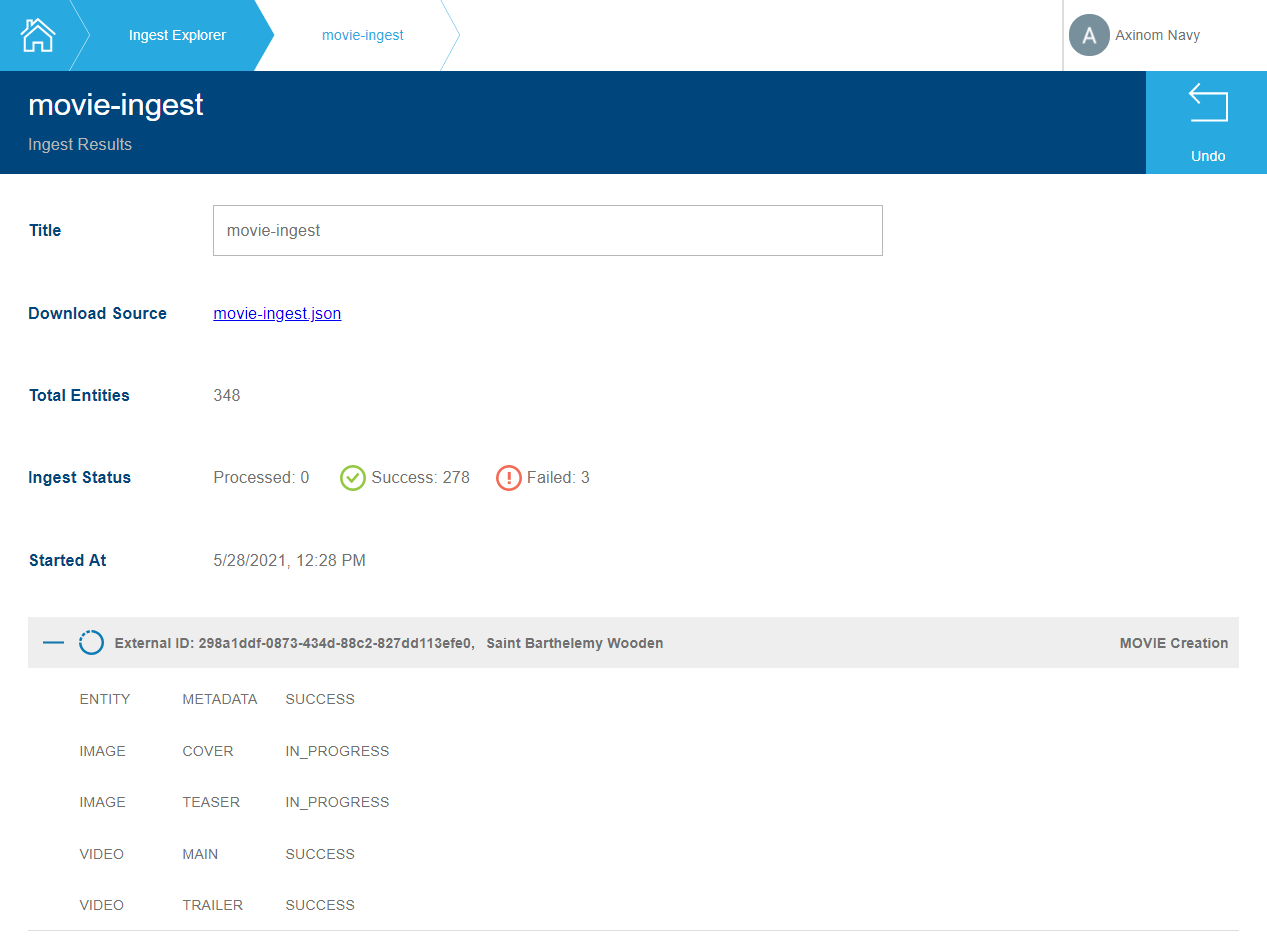
The ingest workflow allows you to see past ingests and start a new one.
The ingest details show the overall state of the ingest progress and
display the ingest items with a detailed view of the progress of the
sub-tasks. The ingest stations can be adjusted under Stations/Ingest.
Mosaic Media Template Ingest Details Workflow
Snapshot Registry
The snapshot registry lists the snapshots that were generated for all
the entities. This gives a good overview of the entities, in case of which the
validation failed and where you need to restart the validation. You could also
get an overview of all entities that were recently published, etc. The details
of a snapshot will lead to the snapshot within the entity it belongs to. This allows
to more easily fix the entity in case of errors. The snapshot registry workflows
consist thus only of an explorer station which can be customized under
Stations/SnapshotRegistry.
Backend
The Node.js backend provides all the GraphQL query and mutation capabilities to manage the OTT media entities. It offers a flexible and customizable GraphQL API that is used by the workflows but can also be used by 3rd party integrations. For the reliable and resilient implementation of background jobs and asynchronous services communication, a message bus based on RabbitMQ is used.
The backend is structured as the domains area and general/cross-cutting concerns.
The domains area contains all the logic that is specific to your entity types
(movies, TV shows, etc.). The other folders contain cross-cutting concerns (e.g.
setting up GraphQL and messaging) or larger topics, such as ingest and publishing
which offer common functionality used in the domain area.
Domains
Domains are the central area to manage the business requirements for the
OTT media management solution. It contains all the entity types and
their specific logic about how they are made available in the GraphQL
API, how they can be ingested, published, or any other related logic. If
you want to adjust something for one specific entity, this is the place where to
do it. Similarly, if you want to add a completely new entity type, this would be
the place where to add it. Code that includes multiple entity types at once resides
in the domains/common folder.
Common examples from the OTT Media Service solution to define one entity type:
- Declare the GraphQL plugins that activate additional functionality in the GraphQL API for the given entity. Among others, this includes GraphQL subscriptions, publishing plugins, bulk operations plugins.
- Message handler implementations to handle entity-type specific RabbitMQ messages. Examples are the ingest handlers to map the ingest document to entity properties and publishing handlers to gather and map all the data for the publishing message.
- Define the permissions for accessing the GraphQL API endpoints of that entity.
- Registration for all the domain-specific message handlers, GraphQL plugins, ingest, publishing, image types, and more.
Finally, the domains folder contains the code to collect all the GraphQL plugins and message handlers, so they can be registered in the startup code. And it contains the logic that maps the operation groups to permissions (e.g. to the admin permission, or the movies view or movies edit permission).
GraphQL
The backend uses PostGraphile to generate its GraphQL API. PostGraphile introspects the PostgreSQL database (tables, columns, relationships, etc.) to create a fast and flexible GraphQL API. You can find more information about PostGraphile and how to best use it in your solutions in our Mosaic developer documentation.
In the Mosaic Media Template, the graphql folder contains the code to set up the
PostGraphile middleware. It allows you to fine-tune all the aspects of how PostGraphile
generates the API and to register your plugins.
The graphql/plugins folder contains mostly plugin factories that provide common
logic to be used for different domain entities.
Messaging
For asynchronous message processing, the Mosaic Media Template uses the Mosaic message bus (with RabbitMQ). The Mosaic message bus uses the notions of events (something happened) and commands (some service should do something).
The main objective of the messaging folder is the setup and registration of the
message handlers and middleware to consume the messages and the setup of publishers to
send out the messages. In addition, there is a media message handler that protects
message handlers by checking the message for specific permissions.
Code in this folder and in the models folder uses the media-messages library
that contains the schema definitions for all events and commands.
Ingest and Orchestration
The OTT Media Service offers ingestion capabilities to import entity metadata into the system. The process takes an ingestion file and will either create new entities or update the existing ones based on a provided unique identifier.
In addition to handling metadata, the system will also orchestrate the ingest of associated assets. For example, a movie is ingested that includes image references and references a main and a teaser video.
The following state diagram shows the ingest process starting from the GraphQL API which receives an ingest document until all items in the ingest were processed.
- The ingestion process is started when a client (e.g. the microfrontend) uploads an ingest document into the GraphQL API endpoint.
- The endpoint validates the JSON file via a JSON schema file to make sure it is in a parseable and valid state.
- If all is fine, it creates a single ingest task that creates sub-tasks for each entity that should be ingested.
- Each ingest item orchestrates the metadata update and related image and video imports for its entity.
- Once all the sub-tasks for an ingest item are done, the ingest item is marked as completed (success or error).
You can find more information in the How-To Guide Start an Ingest and in the Media Service - Ingest documentation.
The ingest folder contains a GraphQL plugins folder with plugins to start the
ingest process and to expose the ingest process details as GraphQL query operations.
The handlers folder contains all the general logic for the metadata ingest via
message handlers and the orchestration of image and video imports into the manage
Image and Video Service. The specific details for the entity metadata mappings are
not in this folder but in the domain area.
Publishing
Publishing is the process of aggregating all entity metadata and exporting it in a self-contained format. Most importantly, it will make the data of the media service (with the related data from other microservices, such as the image and video service) available in the catalog service.
Publishing is done in two steps:
- Generate a snapshot of the entity data and any related data. Run the business validation logic to ensure that all required fields have been correctly filled out.
- Send a message to the catalog service that contains all the relevant data of the entity. The catalog service will subscribe to those messages and update its catalog accordingly.
The publishing process is available for single entities or as bulk operations for
many entities at once. All the core logic to create the publishing GraphQL API
endpoints and the background message handlers is located in the publishing folder.
To learn more about the publishing process, navigate to the Media Service - Publishing documentation.
Publishing Status
Publishing status is a property of publishable entities which helps to easily identify those which are awaiting publication, either because they are not published or because they have changes which are not published. Publishing status is indicated on explorer stations by a colored bar preceding the first column.
Publishing status key
| Explorer Color | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Gray | NOT_PUBLISHED |
This entity is not published. Either it was never published, or it has been unpublished. |
| Green | PUBLISHED |
This entity is published. It has no unpublished changes. |
| Orange | CHANGED |
This entity is published but has unpublished changes. This includes changes to child entities which are included in the published metadata. Changes which are made in another service are not considered (e.g. image or video metadata). |
Publishing a snapshot will not always set the entity’s publishing status to PUBLISHED. If changes were made to the entity since the snapshot was created then the entity’s status will become CHANGED on snapshot publication.
Bootstrap
All the setup and bootstrapping happen in the src/index.ts file. In there, the
express web-server is started. Moreover, there the configuration, database pools,
GraphQL, messaging, logging, monitoring, authentication, etc. are initialized as well.
The package.json file contains the most important scripts to start and test the
application as well as other utility scripts. The entire setup and startup logic
is described in the README.md file.